Business Succession Presentation
Business Planning – Managing Value through Life Insurance
Overview
Business Planning – Case Studies
- Life Insurance Funded Buy-Out
- Family Equalization with Life Insurance
Planning the Business Succession
- Advisor Team
- Information Needed
- Product Guidance
Maintaining the Plan
Take-Aways
- Business Planning Information/Intake Checklist
- Sample Client Audit/Review Letter
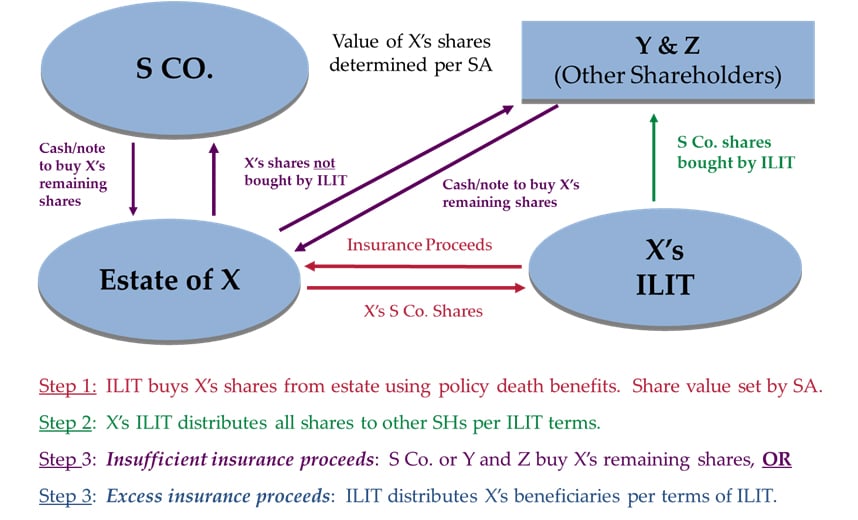
Insurance Funded Buy-Out
Facts
- $100 million S corporation (“S Co.”)
- Owned equally by 3 founders: X, Y and Z
- No current plans to sell S Co.
Objectives
- Facilitate shareholder buy-out at death/disability
- Money/liquidity is always an issue
- Avoid conflicts in buy-out funding
- Upfront cash vs. deferred, longer term-payments from notes
- Implement valuation plan to value shares
- Discounts for minority interests, premiums for control?
- Provide funding for premium payments
- Parity among shareholders whose ages/health may vary
- Minimize estate tax impact of life insurance proceeds on value of business and shareholders’ estates
- Corporate owned – estate inclusion at corporate value level
The Plan
- Separate ILITs
- X, Y, & Z each execute irrevocable life insurance trusts (ILITs)
– Other shareholders must review/approve ILIT form - ILIT terms require trustee to:
– Use life insurance proceeds (up to policy’s face) to buy deceased shareholder’s shares
-Distribute purchased shares to remaining shareholders
-Distribute remaining proceeds to designated ILIT beneficiaries
- X, Y, & Z each execute irrevocable life insurance trusts (ILITs)
- Life Insurance
- Each ILIT buys a $33 million policy on its shareholder
- Shareholder’s Agreement (SA)
- Allows sale of deceased shareholder’s shares to his ILIT
- Allows distribution of shares from ILIT to remaining shareholders
- Requires S Co. or other shareholders to buy any remaining shares of deceased shareholder
– Takes effect only after ILIT uses all proceeds to buy shares
– S. Co./shareholder may fund their purchases with cash, guaranteed promissory notes, based on SA
- Valuation Set by SA
- Critical to set value for shares
– Determines liquidity/funding needs - SA provides that fair market value:
– Is determined by independent expert chosen from agreed-to list of appraisers
– Does not reflect minority discounts / control premiums
- Critical to set value for shares
The Plan – Why?
- Estate Tax Benefits
- Keeps policy proceeds/cash values out of S Co. and owners’ estates
- Fixes estate tax value of shares
- Solves shareholders’ estate liquidity concerns
- Income Tax Benefits
- Shares purchased by ILIT and distributed to other shareholders receive new tax basis equal to purchase price
- Basis increase = capital gains tax savings at later sale of shares
- Conflict Avoidance
- “Automatic” buy-out implementation – policy proceeds pass to ILIT, not other shareholders, so no need to wait on individual actions
- Pre-set valuation method for shares avoids value disagreements
Funding
- Establish 162 bonus plan for each shareholder
- Funds insurance purchase
- Credit for compensation paid
Disability Plan
- Insurance: Each shareholder buys personal disability insurance
- Serves financial planning purposes
- Redemption: S Co. redeems 20% of shareholder’s shares upon disability
- Converts balance to non-voting shares with limited veto powers
Family Equalization with Insurance
Facts
- Father is owner of S corporation
- Has four children
- Three actively employed by business
- One daughter is not (passive)
- Father will not allow a current change of control or reduction in his profit allocation
- Limited lifetime estate/succession planning options
- Wants to treat all children equally
Objectives
- Liquidity
- Estate tax exposure based on father’s retention of business
- Buy-out funding for passive daughter
- Buy-out Planning for Next Generation
- Children/owners work out decision-making process while dad is alive
- Obtain life insurance funding for anticipated business succession while they are young and healthy
- Flexibility in Exit Strategy
- Father may consider sale of business to third party
- Buy-out/funding arrangement must adapt to change in exit plan
Proposal
- Use term product to fund buy-sell if father proposes to sell business in short-term
- Consider mix with a permanent product if plan is to have a legacy based component
- While going through underwriting/examinations, look at survivorship coverage for estate plan and disability insurance
- Ensure all term coverage is convertible to preserve insurability and provide flexibility if exit strategy changes
- Insurance to buy-out daughter/father should be guaranteed to avoid later conflict/litigation
Form Advisory Team
Get Advisors in Place Early
- Successful plan requires multi-prong, coordinated approach
- Producer – insurance planning/coverage needs
- Attorney – structure implementation/documentation
- Accountant – tax treatment and reporting
- Other – financial advisors, appraisers, etc. depending on goals
Get Information
Business Structure & Ownership
- Entity – Type, Location, Organizational Documents
- C corp., S corp., partnership/LLC – can affect tax issues
- Domicile – state tax impact
- Governing documents – By-laws, partnership/operating agreements
- Owners – Number and Percentage Ownership (e.g., cap table)
- Multiple, equal owners – more coverage and cooperation to create succession structure
- Single, majority owner – more flexibility, but consider minority rights, need for equalizing distributions, etc.
- Business – Type
- Service or product oriented
- Key employees
- Corporate, regulatory and/or security requirements – government contractor? Franchise holder?
Goals
- Business Financial
- Maximum income now, reinvest for growth, or make attractive for sale?
- Anticipated Successors
- Transfer to other owners
- Transfer to family members or key employees
- Sale to third party
- Personal
- Financial – retirement, what family needs/wants now
- Estate – what and how much to provide to family later
- Timeframe
- Expected time for exit – during life or at death in months, years?
Existing Arrangements
- Current Coverage in Place
- Policy information
– Type, face amount, cash value, premiums, loans
– Insured, owner, beneficiary
– Intended purpose: buy-out funding, keyman, split-dollar, etc. - Policy performance review/audit
- Policy information
- Related agreements/arrangements
- Existing shareholders, buy-sell and/or trust agreements
- Split dollar, 409A, etc. and prior tax reporting under arrangements
- Employer-Owned Life Insurance (EOLI – IRC §101(j))
- Notice and consent documents – critical, as limited options to correct if proper notice and consent not provided and obtained
- Prior reporting of EOLI policies by business
Suggested Product Options for Business
- Convertible level term for younger owner/key person
- Permanent, survivorship coverage for family (allocate more here for investment component)
- Growing face value for appreciating businesses
- Return of premium riders to address split-dollar issues
Guidance on Existing Coverage
- 1035 exchange
- Surrender
- Keep
- Reduce face amount
Maintaining the Succession Plan
Provide On-Going Support
Post-closing support is critical to succession planning:
- Plan and coverage must adapt to changes in:
- Business value and ownership (owner departure/entry)
- Owner’s age and health status/condition (e.g., quit smoking, illness)
- Tax laws
- Need continual monitoring to maintain and meet objectives:
- Monitoring cost of insurance for split-dollar plans
- Tracking term conversion rights
- Reviewing and providing updates on policy performance (e.g., is cash value product performing to meet deferred comp objectives?)
- Provide reminders of reporting requirements to attorneys/CPAs
- Apprise of carrier changes (crediting rates, pricing, risk classifications)
- Coordinate with other advisors to remain updated on technical and business developments
- Consider a “tickle” system for annual review of plans/products




